Google RankBrain: The Complete Guide (Everything You Need to Know & More)
Today we’re teaching you everything you need to know about Googles RankBrain algorithm.
From how RankBrain works to how it effects SEO. Find out everything you need to know and more here in our complete guide.
What is Google RankBrain?
Google RankBrain is a machine learning algorithm which uses artificial intelligence to help sort search results. After being named Googles third most important signal for search queries, RankBrain has become a core part of Googles algorithm. Its main role is to understand users search queries and deliver relevant results based off the words searched.
Machine Learning vs Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning (ML) is the capability a machine has to analyse data and in turn, teach itself. This can be as simple as learning what a user is really looking for when they spell their search query wrong or as complex as analysing a search query and working out what the user really means.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a development in computer science which creates machines that are capable of intelligent behaviour.
The difference between ML and AI is that artificial intelligence is the broader base of a smart machine, however it is the machine learning capabilities which gives the machine its intelligence.
How does RankBrain work?
RankBrain is designed to understand what a user is searching for, even if they are not using the exact words needed for that search query as well as use other aspects such as user location and context to ultimately provide relevant search results.
In other words, it helps to understand the intent of a users search and provide results based on this. To do this, Google feeds RankBrain endless quantities of data, which include users’ locations, history and device, in order for the system to teach itself what search results to provide.
RankBrain Examples:
If a user types in the search query ‘world cup location’ into Google, the system first tries to identify the true intent of the search. For this search term, it would consider factors such as the user’s location and history as well as considering if they are searching for the location of the most recent World Cup or the upcoming one.
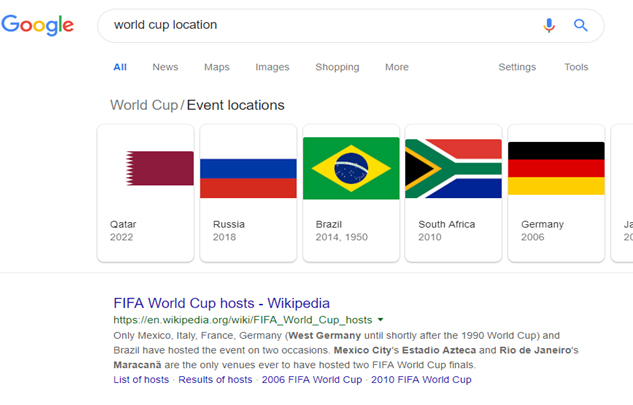
As well as taking factors of the individual users into account, RankBrain also considers patterns it has picked up through users searches. Therefore when requesting the ‘world cup location’ RankBrain will look into its database and provide you with the result below.
This result, therefore, caters for all users as it not only provides them with the next world cup location but also previous ones. This result may vary however depending on where the user is searching from, i.e. if they are in the city of the world cup, it may provide them driving directions to the event.
Another example of the Google RankBrain algorithm is when a user searches for ‘Where should I go for dinner?’. Using its intelligence, RankBrain understands that you are looking for a restaurant to eat at and takes factors such as your location into consideration to provide you with relevant results that are local to you.
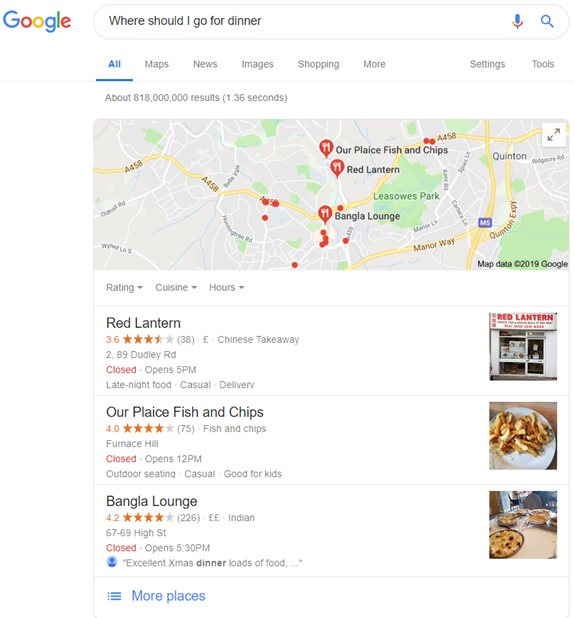
The above shows how RankBrain has used our location and in turn, provided us with results relevant to us.
How does RankBrain decide what to rank?
RankBrain decides how to rank results simply by recording how satisfied they believe Google users are by the pages they land on as well as the importance of backlinks linking to a page, the content freshness and domain authority.
For example, a Google user searches
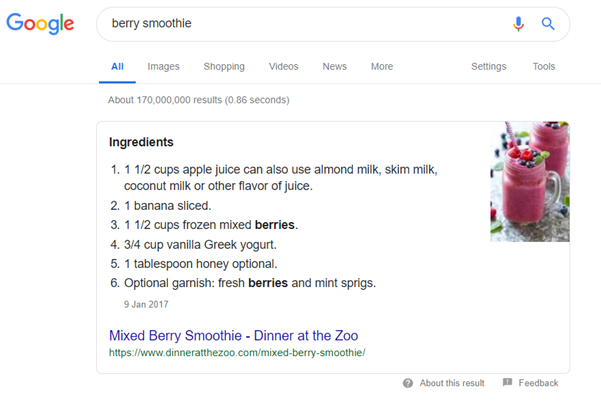
Firstly, Google presents you with a result positioned at what is referred to as ‘Position Zero’. RankBrain will have positioned this result here as it has noted user’s behaviour towards this website. Factors the Google algorithm takes into consideration are the website chosen by the user and the time the user spends on the website.
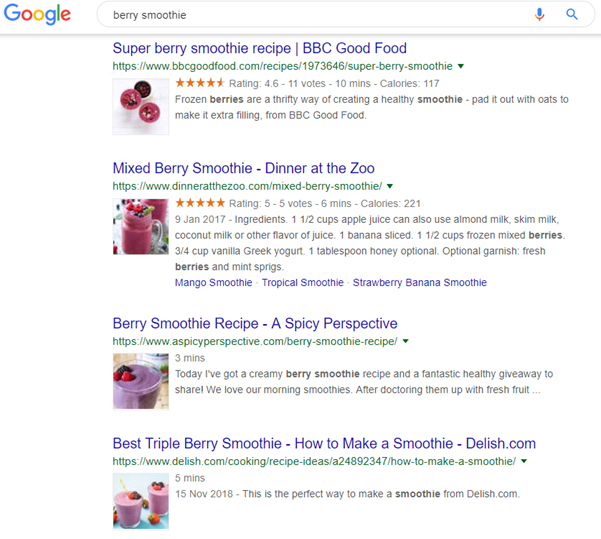
The above shows how Google has ranked websites in accordance to the search query ‘berry smoothie’.
It ranks these websites again by looking at user behaviour. If a user chooses a website but bounces straight off it, the algorithm will take a note of this and presume the website wasn’t very useful and in turn rank it lower. When the Google RankBrain algorithm records people bouncing from site to site, they call this ‘pogo-sticking’. However, if a user spends a sufficient amount of time on the website, it will know that the content on this website was useful and therefore rank it higher in the future.
What did Google do before RankBrain?
Before RankBrain, Google was capable of finding pages beyond the exact terms a user used in a searching query. Previous to the Google RankBrain algorithm, Google developed itself so it could recognise variations of the same search queries in order to provide relevant results to their users. It also understood words had synonyms so if someone searched for ‘workout clothes’ it understood the user was looking for ‘gym wear’.
Now RankBrain is in place, it allows Google to understand more complex search terms and interpret them effectively. In 2013, Google stated that 15% of the search queries they found had never been seen before, which was a reduction from the 20-25% in 2007. RankBrain helps to link search queries together so they can provide users with the results they were looking for.

RankBrain in SEO
Dwell Time and Bounce Rate
Dwell time refers to the amount of time a user spends on a website after clicking on it from the results they were provided.
In simple terms, the longer a user spends on a website the more likely it is to be ranked higher by Google.
There are a number of techniques you can practice to boost your dwell time. These include:
Content Length – In short, longer content leads to a better dwell time. If you can create a piece of content which answers all the questions a user may ask, then it decreases the probability that the user will bounce of your website and find another to answer their questions.
For example:
It’s the start of the new year and your resolution is to get fitter, so you search for ‘how to start the gym’. The first article you may come across is a short 350-word article that starts to answer your questions but doesn’t totally fulfil what you’re looking for. So you bounce of this website and look for one with more content to further answer your questions.
Then, you find the website you’ve been looking for. An online guide with work outs for beginners, dietary advice and even tutorials showing how to perform certain exercises. So you spend a significant amount of time looking through this guide, re-reading some parts and taking in all the information it has to offer.
This increases the dwell time on this site compared to the first one you selected and in turn shows Google that the second website should be ranked higher.
Importance of Brand Awareness
Brand awareness is an important factor when increasing your click through rate (CTR). If people recognise your brand it immediately increases the probability of a user clicking onto your website. Seeing a brand they know will increase the trust in a website and make the user more comfortable when using the website.
What Factors Apply to Your Content?
An important thing to bear in mind is that RankBrain has a collection of factors it takes into account when ranking search results. It is important to identify what which of these factors best apply to your content and optimise your content accordingly. Some of the ranking factors include:
• Content depth
• Freshness of content
• Diversity of backlinks
• User engagement (dwell time and bounce rate)
• User location
• The user’s device
The best way to optimise your content in accordance to these factors is to review the topic your covering and its urgency.
For example:
If your uploading an article in relation to a recent crime in an area, the content freshness is a key factor as well as the sure engagement. However, if your writing content on the history of the Black Country, the depth of this content will be more important to the user and Rank Brain.
Thorough Content is Key
In the past, a common SEO technique was to have individual pages for each keyword. So if you was selling security cameras there would be an individual page created for ‘CCTV cameras’, ‘CCTV camera’, ‘Security cameras’ and all the other commonly searched terms surrounding the service.
SEO has since moved on from this and Google is now favouring pages with longer content containing everything the user is searching for. This means incorporating all key words and phrases in one in depth piece of content that speaks to the user in a natural tone.









